Report On the State
of the Environment In China
2 0 0 4
Environmental Management
- International cooperation and exchanges on environmental protection
- Laws, regulations and rules on environmental protection
- Major environmental pollution accidents in 2004
- Creating national environmental friendly enterprises
- Quantitative examination of comprehensive control of urban environment
- Environmental management of construction projects
- Environmental emergency exercise in 2004
- Major water pollution accident in Tuojiang River and its investigation
- Building eco-sound provinces (cities, counties)
- Establish National Model on Environmental Protection and National Environmentally Beautiful Towns
- Crack down on illegal environmental behaviors and carry out campaign to rectify corporate behavior for environmental protection
- Investment in the control of environmental pollution of China
- Management of the import and export of chemicals
- Development and protection of geothermal resources
- Standards, norms and technical requirements for environmental protection
- Construction of urban infrastructure
- Geological parks
- Pollution losses of the fishery industry
- Environmental protection of the mining industry
- Pilot implementation of early-warning signals for unexpected meteorological disasters
- Improving water supply and lavatory facilities in rural areas
- Prevention and control of endemic diseases
International cooperation and exchanges on environmental protection
|
In 2004, state leaders President Hu Jintao, NPC Chairman Wu Bangguo, Premier Wen Jiabao, Vice Premier Zeng Peiyan and NPC Vice Chairman Gu Xiulian attended activities of international environmental protection on eight occasions. SEPA organized and arranged over 90 major activities on international environmental cooperation, and sponsored 35 international conferences of varied scales in China. SEPA also brought in and put in place foreign funds at around $118.5 million through bilateral and multilateral cooperation, China Council for International Cooperation on Environment and Development (CCICED) and other channels. All together 260 persons were dispatched by SEPA to attend bilateral, multilateral and regional environmental consultations and negotiations; 31 environmental delegations from abroad at or above ministerial level visited China on the invitation of SEPA. In addition, SEPA signed 6 new memoranda or letters of intent on bilateral cooperation with Italy, Czech, Hungary and other countries. The Third Meeting of the Third Phase China Council for International Cooperation on Environment and Development (CCICED) was held during October 29 - 31, 2004. Premier Wen Jiabao met both the Chinese and international Council members, and listened to the policy recommendations on China's sustainable development of agriculture and rural areas. Vice Premier and CCICED Chairman Zeng Peiyan presented at the meeting and delivered an important speech. On October 12, 2004, in accompany of Mr. Xie Zhenhua, Minister of SEPA and Mr. Wang Guangya, Permanent Representative of China to the United Nations, UN Secretary General Kofi Anan visited China's First Eco-Agriculture Village, Liuminying Village in Daxing County, Beijing. |
Laws, Regulations and Rules on Environmental Protection
|
On December 29, 2004,the National People's Congress amended and promulgated the Law of People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution Caused by Solid Waste. The State Council issued Measures on the Management of Operation Permits of Hazardous Waste on May 30, 2004. The State Environmental Protection Administration issued Provisions for Imposing Administrative Penalties Concerning the Management of Medical Wastes, Provisions Concerning the Administration of Bulk Cement and Provisional Provisions Concerning the Examination and Approval of Cleaner Production together with other relevant ministries; the State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) also released Measures for Administration of Environmental Pollution Treatment. |
Major environmental pollution accidents in 2004
|
SEPA received altogether 67 reports of environmental accidents in 2004, 6 of which were extremely serious and 13 were serious accidents, causing 21 dead and 705 poisoned or injured with direct economic losses over 550 million yuan. Compared with last year, this year saw three more accidents, but a reduction of 216 in death toll (the severe gas well accidents happening in Kai County, Chongqing Municipality in 2003 caused 234 dead) and 50 million yuan less in direct economic losses. In 2004, 28 ship pollution accidents with a single spill over 0.1 ton occurred within Chinese sea areas, mainly oil spills totaling around 3,817 tons. Among those accidents, 15 had a single spill amounting to over 10 tons and 3 over 50 tons. All the above-mentioned accidents had been properly handled. |
Creating national environmental friendly enterprises
 |
SEPA held a grand awarding ceremony at the Great Hall of the People on November 16, 2004 and the following eight enterprises were the first group winning 'National environmental friendly enterprises': Bayer (Wuxi) Leather Chemical Co., Ltd., Shandong Lubei Group Co., Qingdao Port Group Co., Ltd., Jindong Paper Industry (Jiangsu) Co. Ltd.,Sinopec Zhenhai Refining & Chemical Co. Ltd., Kunshan Banknote Paper Mill, Nantong Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd., and Dushanzi Petrochemical Company of Petro-China Co. Ltd.. |
Quantitative examination of comprehensive control of urban environment
|
SEPA reformed the application, examination, approval and release practice on quantitative examination of comprehensive control of urban environment in 2004. Up to 500 cities would formally submit the examination results to the upper authority, accounting for 75% of the total cities in mainland China. 66 new cities were added to the list of national level key cities on environmental protection, making the total number of national key cities on environmental protection increased 47 to 113, which are required to make public the examination results by the State. It was the first time that China had released the ranking of cities in terms of the quantitative examination results of cities within the jurisdiction of each province, autonomous region and municipality. |
Environmental Management of Construction Projects
|
According to the plan of the State Council, relevant departments under the State Council carried out streamlining work on fixed-assets investment projects. In the order of 55,024 construction projects had been investigated. Among them, 51,117 were in conformity with environmental protection requirements and the other 1,190 were not. SEPA had found that 45 construction projects including Guangdong Hengdali Cement Plant and petroleum development project of Ordovician, No. 7 of Tahe Oil Field in Tarim Basin, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, started their construction work before the EIA statements had not been approved, and given due punishment
to those projects. SEPA also launched special campaigns to check the implementation of
'Three Simultaneities' of construction projects that were approved during 1998 to 2002; 220,673
construction projects were under such investigations, among them, 1,539 were notified to go
through the make-up check and acceptance procedures for environmental protection within a given
period and the other 2,378 projects had went through such make-up procedures as required. 1,478
enterprises in violation of EIA law and the 'Three Simultaneities' system had been put on
record, investigated and punished. |
Environmental Emergency Exercise in 2004
|
The State Environmental Protection Administration, together with People's Government of Ningbo City, launched an environmental emergency exercise on October 27, 2004. It simulated a pollution incidence caused by leakages of toxic materials due to the failure of the control equipments in a large chemical enterprise in Ningbo city, leading to severe local air pollution. When local environmental protection department received the report of the accident through 12369-the environmental hotline, it dispatched an emergency team in charge of environmental supervision and monitoring to address the accident. Meanwhile Ningbo Municipal Government instructed other relevant departments to provide first aids. SEPA established an Exercise Headquarter in Beijing, which took charge of the dispatch and handling of the accident. Upon receiving the report, the Headquarter started the emergency preparedness plan, successfully delivered long-distance instructions to control and finally eliminate the contamination with the help of such tools as environmental emergency commanding system, information transmitting system, decision-making support system, internet, satellite positioning system and special line transmitting technology. |
Major water pollution accident in Tuojiang River and its investigations
|
In March 2004, Sichuan Chemical Co. Ltd. went against the
'Three Simultaneities' system, forced production without prior reporting to the local environmental protection organizations and
when
the desorption equipments failed to work normally. Consequently, a large amount of
wastewater
containing high-concentration ammonia and nitrogen was discharged directly outside
of the plant;
the sewage entered Tuojiang River through its tributary Pi River and polluted the
water
seriously. From March 2, 2004 on, dead fish appeared in Tuojiang River and Jianyang,
Ziyang,
Zizhong and Neijiang, four cities (or regions) along Tuojiang River suffered from potable
water
sources pollution. By March 26 when the pollution was under control, the number of dead
fish had
amounted to one million kilograms in the lower reaches of Tuojiang River; nearly one
million
people had suffered from a 25-day break of drinking water supply and aquatic
eco-environment of
Tuojiang River had undergone great damages. A large number of industries,
companies and service
sectors ceased operation and business, which resulted in a direct loss up to more than 219
million yuan as estimated by Sichuan Province. When the accident occurred, leaderships from the
State Council and SEPA attached great significance to it and delivered important written
instructions respectively. The CPC Sichuan Provincial Committee and the provincial government
took measures promptly. They transferred domestic water and Min River water to wash away the
sewage, found ways to meet the water supply of the people concerned and finally eliminated the
pollution. |
Building of Eco-Sound Provinces (Cities and Counties)
|
By the end of 2004, eight provinces had carried out the campaign to build eco-sound provinces, namely Hainan, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Zhejiang, Shandong, Anhui, Jiangsu and Fujian. A batch of cities (districts) and counties had also launched the building of eco sound cities (districts) and counties including Ningbo, Qingdao, Shenzhen, Xiamen, Hangzhou, Changsha, Nanjing, Suzhou, Yangzhou, Shaoxing, Panjin, Yancheng, Quzhou, Zhongshan, Zhoushan, Huaihua, Huangshan, Ma'anshan, Wuxi, Haining, Anji, Changshu, Zhangjiagang, Kunshan, Jiangyin, Minhang Dist. of Shanghai, Chaoyang Dist. of Beijing, Longgang Dist. of Shenzhen and Dujiangyan. State Environmental Protection Administration examined 84 pilot areas and units of ecological demonstration zone for check and acceptance and the number of state level ecological demonstration zone has reached 166. |
|
In 2004, State Environmental Protection Administration conducted technical examination on a few cities including Weifang, Rizhao, Penglai, Jiaonan and Laixi of Shandong province, Fuyang of Zhejiang, Guilin of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Chengdu of Sichuan and Baoji of Shannxi to review their technologies for NMCEP or to check before approval. 12 cities (districts have won the title of NMCEP successively, which set a record of the number of nominated cities since the NMCEP campaign was launched in 1997. The 12 cities (districts) included Mianyang, Wuxi, Jintan, Liyang, Fuzhou, Zhenjiang, Changzhou, Shenyang, Karamay, Kuerle, Jiangmen and Yubei Dist. of Chongqing. By the end of 2004, 44 NMCEPs and 3 National Model City Districts on Environmental Protection had been nominated. And over 100 cities and districts involving 23 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities are striving to won the title of NMCEP. In 2004, 38 towns including Changgou Town of Fangshan District, Beijing were given the title of National Environmental Beautiful Town and Changshan County of Zhejiang, Zhujie Town of Qujing, Yunnan were given the title of National Environmental Beautiful Town by SEPA. Up to now, 79 National Environmental Beautiful Towns have been nominated. |
|
 |
Mr. Xie Zhenhua, Minister of SEPA, awarded Nanjing the title of NMCEP. |
|
A special campaign targeting enterprises discharging pollutants illegally was launched nation wide from April of 2004 to Nov. 2004 through the joint efforts by State Environmental Protection Administration, NDRC, Ministry of Supervision, State Administration for Industry and Commerce, Ministry of Justice and State Administration of Work Safety. This campaign was to safeguard people's health and to protect the environment. The seven-month campaign has involved 1.31 million person time of law enforcers, examined 600,000 enterprises and addressed 3,365 serious environmental cases by urging local authority to solve the problems on list under supervision (425 cases were under the supervision of provincial authorities). Over 100 problems concerning pollution on a large scale were harnessed and 27,000 illegal environmental cases were placed on file for investigation. During this combat, 6,462 enterprises discharging pollutants illegally were banned or ordered to close, 3,861 enterprises were ordered to stop production for rectification and 6,755 enterprises were demanded to rectify their problems within a given time limit. 155 persons responsible were punished, 81 of them were from local governments and departments concerned. A great deal of facilities and enterprises were examined during the campaign, including 587 urban sewage treatment plants, 772 garbage disposal facilities, 45,000 large livestock and poultry breeding farms and 9,880 enterprises from such key sectors as iron & steel, electrolytic aluminum, cement, calcium carbide, coking, ferroalloy, chrome salt, yellow ginger and rechargeable batteries. 729,000 newly built projects since 2000 were involved. State Environmental Protection Administration has dispatched 19 secret investigation teams to supervise local authorities on the handling of the following cases: rebounding of pollution in Huaihe River basin, pollution accident of Tuojiang river of Sichuan Province, algal bloom of the tributaries of the Three Gorges reservoir, pollution caused by steel plants of Tangshan in Hebei, lead pollution in Xushui County of Hebei and Changxing County of Zhejiang, etc. Governments at all levels have overseen their departments responsible to handle the 3,365 pollution cases on list with severe threats to health and the environment. Among them, 425 cases were under the supervision of provincial authorities. A 400,000 m3 slag mountain in Qitaihe City of Heilongjiang Province was moved away, which has solved the drinking water safety problem that had long plagued the local residents. Guyan City of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region also took concrete measures to ban Guyuan Wangheng Paper Mill that had affected drinking water sources for the residents in Jingning County, Gansu Province, averting a trans-boundary pollution dispute. Zhejiang government has carried out concentrated rectification for rechargeable batteries enterprises in Changxing County, which caused over 500 children suffering from lead poisoning. As a result, 115 enterprises incapable of pollution were shutdown. In Jiangxi Province, 5 unlicensed refineries which once imposed health risks to local teachers and students at Jiangxiang Town of Nanchang County, were suppressed. In Hebei Province, 11 enterprises engaged in lead production at Xushui County were all banned and the legal representatives of four unlawful enterprises were detained according to law. The county magistrate and the vice magistrate in charge of relevant affairs of Xushui County were prosecuted for administrative responsibilities. |
Investment in the Control of Environmental Pollution of China
|
In 2004 the total investment in controlling environmental pollution in China was valued at 190.86 billion yuan, up by 17.3% against the previous year. Of the total investment, 114 billion yuan was spent on urban environmental infrastructure, a 6.3% increase over the previous year while 30.81 billion was for controlling industrial pollution sources. The environmental investment of new construction projects amounted to 46.05 billion in order to implement the "Three simultaneities" policy, an increase of 38.1% against the previous year. In 2004 the investment in controlling environmental pollution took up 1.40% of GDP, same as 2003. |
Management of the Import and Export of Chemicals
|
The year 2004 was the first year since the promulgation of Measures on Environmental
Management
of New Chemical Substances. A total of 317 kinds of substances were approved exempt from
declaration during the year, 20 applications were accepted and 2 new substances
had passed the
review. State Environmental Protection Administration announced the List of Chemicals Imported to
or Produced in People's Republic of China, which included over 4,300 kinds of substances. A
professional reviewing committee for new chemical substances was established, the registration
work of new chemicals enjoyed a good beginning and a new chemicals registration system in
conformity with international practice has been developed. |
Development and Protection of Geothermal Resources
|
There are 103 geothermal fields prospected across China with a total available resource of 333
million m3/year. The available total geothermal water resources reached 6.717 billion
m3/year with available heat of 962.28´1015 joule, equal to 32.834 million tons of coal equivalent. |
Standards, Norms and Technical Requirements for Environmental Protection
|
In 2004, 7 national standards for environmental protection were promulgated including the Standards for the Discharge of Air Pollutants of the Cement Industry, Discharging Standards of Pollutants of the Citric Acid Industry, Discharging Standard of Pollutants for the Monosodium Glutamate Industry, Standards on the Concentration of Air Pollutants Resulting from Destroying the Chemical Weapons Abandoned by the Japanese Invaders During WW I (Draft), Standards on the Concentration of Surface Water Pollutants Resulting from Destroying the Chemical Weapons Abandoned by the Japanese Invaders During WW II (Draft), Standards on the Concentration of Underground Water Pollutants Resulting from Destroying the Chemical Weapons Abandoned by the Japanese Invaders During WW II (Draft), Standards on the Concentration of Soil Pollutants Resulting from Destroying the Chemical Weapons Abandoned by the Japanese Invaders During WW II (Draft). 17 industrial standards for environmental protection were promulgated such as Standards on the Acoustic Design and Measurement of Sound Barrier. Measures on the Management of the File on Local Environmental Standard and Pollutant Discharge Standards was also released. The authority had issued 15 technical requirements for environmental products. |
Construction of Urban Infrastructure
|
There were 661 cities by the end of 2004 with urban population of 340.88 million. Urban area covered 394,200
km2, among them, 30,300 km2 were built area. The population density in urban area was 847 persons per
km2. |
|
In 2004, 41 new national geological parks were approved, raising the total number to 85 across the country. Among them, 8 geological parks such as Huangshan Mountain in Anhui Province, Lushan
Mountain in Jiangxi, Yuntaishan Mountain in Henan, the Limestone Tower in Yunnan, Danxia Hill in
Guangdong, Zhangjiajie Scenic Spot in Hunan and the Five Great Chain Lakes in Heilongjiang
province were the first group listed in the World Geological Park Network Catalogue. |
Pollution Losses of the Fishery Industry
|
In 2004, there were altogether 1020 pollution accidents in the fishery industry nationwide, causing direct economic losses of 1.08 billion yuan RMB. Among them, 79 were marine pollution accidents covering an area of 28,000 ha and causing direct economic losses of about 890 million yuan RMB; and 7 were very big pollution accidents (with loss of over 10 million yuan RMB). In the same year, there were 941 inland waters pollution accidents covering around 211,000 ha with direct economic losses of 190 million yuan RMB. Among them, 3 were very big pollution accidents with the economic loss of each one over 10 million yuan RMB, and 14 were big accidents with the loss of each over 1 million yuan. In 2004, the countable economic losses in natural fishery resources imposed by environmental pollution totaled 3.65 billion yuan RMB, among them, the losses of inland fishery resources were 860 million yuan and marine fishery resources 2.79 billion yuan. |
Environmental Protection of the Mining Industry
|
In 2004, legislation and institutional study on environmental protection of mines were reinforced, and the application work of National Mine Parks was initiated. |
Pilot Implementation of Pre-warning Signals for Unexpected Meteorological Disasters
|
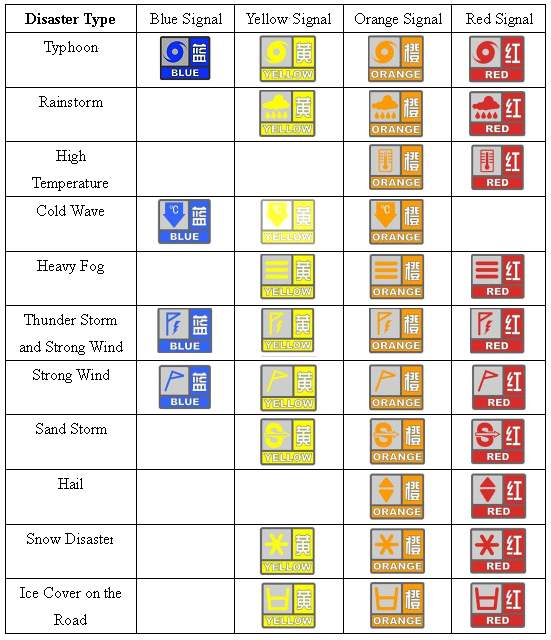
China National Meteorological Administration formulated the Provisional Measures on the Implementation of Pre-warning Signals for Unexpected Meteorological Disasters on August 16th of 2004. The pre-warning signals included 11 types including that for typhoon, rainstorm, high temperature, cold spell, heavy fog, thunder storm and strong wind, strong wind, sand storm, hail, snow disaster and ice cover on the road. The warming signals generally were classified into four grades (IV, III, II and I), i.e. general, fairly severe, severe and very severe. The four grade were marked by the color of blue, yellow, orange and red respectively and were labeled in both Chinese and English. Pre-warning Signals for Unexpected Meteorological Disasters
|
Improving Water Supply and Lavatory Facilities in Rural Areas
|
By the end of 2004, 53.1% of the 248 million rural households nationwide had built various types of sanitary lavatories, and 60% of the 945 million of rural population had access to tap water. The work of upgrading water supply in the rural areas in 2004 paid special attention to water quality monitoring in a bid to raise water quality which was conducive to sanitation and disease prevention. In 2004, the Central Government allocated a special fund of RMB 107 million yuan for the construction of sanitary lavatories for rural households and the capacity building in water supply and good lavatory facilities in order to reinforce the water supply and lavatory transformation work in rural areas. The project covered 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) as well as the Xingjiang Production and Construction Corps. |
Prevention and Control of Endemic Diseases
|
By the end of 2004, 326 counties had been classified as Keshan disease areas with accumulated 256 counties under basic control of such disease; 354 counties had been identified as Kaschin-Beck disease areas with accumulated 196 counties under basic control; 2812 counties were under the iodine-deficiency monitoring, with accumulated 2329 counties having eradicated or basically eradicated such disease. In addition, among the 113,742 villages of 1,108 counties suffering from endemic fluorine poisoning (from drinking water), 50,617 villages had their water supply improved, benefiting a total of 40,646,000 rural residents. Among the 7,990,000 rural households of 200 counties with fluorine poisoning (from coal-burning pollution) endemic, 2,030,000 households had transformed their kitchen stoves, benefiting a total population of 8,067,000. Among the 388 villages of 28 counties with arsenic poisoning (from drinking water) endemic, 253 villages had improved their water supply, benefiting a total of 283,000 people. There were 7,500 rural households suffering from arsenic poisoning (from coal-burning pollution) endemic in 12 counties, 2,623 of which had transformed their kitchen stove, benefiting 8,400 people. In order to strengthen the work of prevention and cure of endemic diseases, 120 million yuan RMB of fund was earmarked by the Central Government for the prevention and cure of key endemic diseases including iodine-deficiency, fluorine and arsenic poisoning, Kaschin-Beck and Keshan diseases. The project covered 29 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), focusing mainly on kitchen stove transformation for the prevention of endemic fluorine poisoning, water quality monitoring in fluorine and arsenic-poisoning-stricken areas, investigation of high-iodine water sources and the monitoring on the Kaschin-Beck and Keshan diseases. |
Environmental Management